Rural City of Wangaratta
About the profile areas
The 2023 Estimated Resident Population for the Rural City of Wangaratta is 30,002, with a population density of 8.23 persons per square km.
Location and boundaries
The Rural City of Wangaratta is located in north-eastern Victoria, about 235 kilometres north-east of the Melbourne CBD. The Rural City of Wangaratta is bounded by Indigo Shire in the north, Alpine Shire in the east, Wellington Shire and Mansfield Shire in the south, and Benalla Rural City and Moira Shire in the west.
Traditional Owners
The original inhabitants of the Rural City of Wangaratta were the Pangerang and Ya-itma-thang Aboriginal people.
Name origin
The Rural City of Wangaratta is thought to be named from an Aboriginal word meaning "nesting place of cormorants".
Important
|
Population30,002 2023 ABS ERP |
Land area3,644 square km |
Population density8.23 persons per square km |
Settlement history
European settlement dates from the late 1830s, with land used mainly for grazing and crop growing. The township of Wangaratta was laid out in 1849, developing as a service centre to the surrounding farming district. Growth took place from the late 1850s, largely due to gold discoveries in the Ovens Valley, with mining in Eldorado until 1954. Several small townships were established from the 1850s to the 1870s, including Glenrowan, Milawa, Moyhu, Oxley and Springhurst. More substantial population growth took place during the late 1800s, aided by the opening of the railway line from Melbourne in 1873 and industrial growth. Rapid growth took place in the immediate post-war years, with growth through to the late 1970s. The population declined slightly during the 1980s and 1990s, and then increased marginally from the early 2000s.
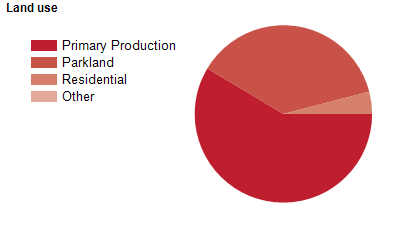
Land use
The Rural City of Wangaratta is predominantly a rural area, but has significant residential areas in and around the city of Wangaratta. Smaller townships include Eldorado, Everton, Glenrowan, Milawa, Moyhu, Oxley, Peechelba, Springhurst, Tarrawingee, Whitfield and Whorouly. The Rural City encompasses a total land area of about 3,600 square kilometres, including substantial areas of national park. Rural land is used largely for agriculture, including viticulture.
Transport
The Rural City of Wangaratta is served by the Hume Freeway, the Murray Valley Highway, the Great Alpine Road and the Melbourne to Wodonga railway line.
Major features
- Major features of the Rural City of Wangaratta include Alpine National Park,
- Chiltern-Mt Pilot National Park,
- Warby-Ovens National Park,
- The Wangaratta CBD,
- Goulburn Ovens Institute of TAFE (Wangaratta Docker Street and Regional Study Centre),
- The Murray to Mountains Rail Trail,
- Wangaratta Racecourse,
- Wangaratta Indoor Sports and Aquatic Centre,
- Northeast Health Wangaratta,
- Wangaratta Art Gallery,
- Wangaratta Performing Arts Centre,
- The Ovens River,
- The King River and various wineries.
Included areas
- The Rural City of Wangaratta includes the localities of Archerton (part),
- Bobinawarrah,
- Boorhaman,
- Boorhaman East,
- Boorhaman North,
- Boralma,
- Boweya (part),
- Bowmans Forest,
- Bowser,
- Byawatha,
- Carboor,
- Cheshunt,
- Cheshunt South,
- Docker,
- Dockers Plains,
- East Wangaratta,
- Edi,
- Edi Upper,
- Eldorado,
- Everton,
- Everton Upper,
- Glenrowan (part),
- Greta,
- Greta South,
- Greta West,
- Hansonville,
- Killawarra,
- King Valley,
- Laceby,
- Londrigan,
- Markwood,
- Meadow Creek,
- Milawa,
- Moyhu,
- Murmungee,
- Myrrhee (part),
- North Wangaratta,
- Oxley,
- Oxley Flats,
- Peechelba (part),
- Peechelba East,
- Rose River,
- Springhurst,
- Tarrawingee,
- Tolmie (part),
- Upper Lurg (part),
- Wabonga,
- Waldara,
- Wangandary,
- Wangaratta,
- Wangaratta South,
- Whitfield,
- Whitlands,
- Whorouly,
- Whorouly East and Whorouly South.