Derwent Valley Council area
About the profile areas
The 2023 Estimated Resident Population for the Derwent Valley Council area is 11,341, with a population density of 2.77 persons per square km.
Location and boundaries
The Derwent Valley Council area is located in southern Tasmania, about 30 kilometres north-west of the Hobart CBD. The Derwent Valley Council area is bounded by the Central Highlands Council area in the north, the Southern Midlands Council area, the Brighton Council area and Glenorchy City in the east, the Huon Valley Council area in the south, and the West Coast Council area in the west.
Traditional Owners
The original inhabitants of the Derwent Valley area were the Big River (midlands) Aboriginal people.
Name origin
Derwent Valley is named after the Derwent River, which was named after the River Derwent in the Lakes District of England.
Important
|
Population11,341 2023 ABS ERP |
Land area4,101 square km |
Population density2.77 persons per square km |
Settlement history
European settlement dates from 1807 when Norfolk Islanders arrived, attracted by the fertile farm land and reliable water sources. The township of Elizabeth Town (now New Norfolk) was established in 1811 following Governor Macquarie’s visit to the area. The first road to Hobart was constructed in 1818. Hop growing commenced from the late 1840s, and continues as an important industry today. Growth took place during the late 1800s, aided by the opening of the railway line to Hobart in 1887. A paper mill was established in Boyer in 1941, with a timber milling township at Maydena from the 1940s to the 1980s. The township of Strathgordon was established in the late 1960s for the Hydro Tasmania workers who worked on the flooding of Lake Pedder in 1972 to create a hydro-electric scheme. The population of the Council area declined slightly during the 1990s, falling from about 10,000 in 1991 to about 9,000 in 2001. The population then increased marginally, rising to nearly 9,600 in 2011.
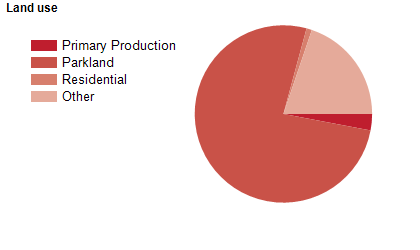
Land use
The Derwent Valley Council area features both rural and township areas. The main township is New Norfolk, with several smaller towns. Rural land is used largely for beef and sheep farming, forestry and hop growing, with some other agricultural industries. The Council area encompasses a total land area of over 4,100 square kilometres.
Transport
The Derwent Valley Council area is served by the Lyell Highway.
Major features
- Major features of the Council area include Franklin-Gordon Wild Rivers National Park,
- Mount Field National Park,
- Southwest National Park,
- Lake Gordon,
- Lake Pedder,
- The Derwent River,
- various state forests,
- Norske Skog Boyer Paper Mill,
- Derwent Valley Sport and Recreation Centre,
- New Norfolk Golf Club,
- New Norfolk District Hospital,
- Millbrook Rise Hospital,
- Bushy Park Estates (hop fields),
- Lake Pedder Chalet and Salmon Ponds Heritage Hatchery & Gardens.
Included areas
- The Derwent Valley Council area includes the townships and localities of Black Hills (part),
- Boyer (part),
- Broadmarsh (part),
- Bushy Park,
- Claremont (part),
- Collinsvale (part),
- Fitzgerald,
- Florentine (part),
- Glenfern,
- Glenlusk (part),
- Glenora,
- Granton (part),
- Gretna (part),
- Hayes,
- Karanja,
- Lachlan,
- Lawitta,
- Macquarie Plains,
- Magra (part),
- Malbina,
- Maydena,
- Molesworth,
- Moogara,
- Mount Field (part),
- Mount Lloyd,
- National Park (part),
- New Norfolk,
- Plenty,
- Rosegarland,
- Sorell Creek,
- South West (part),
- Strathgordon,
- Styx,
- Tyenna,
- Uxbridge,
- Wellington Park (part) and Westerway (part).