City of Ballarat
About the profile areas
The 2023 Estimated Resident Population for the City of Ballarat is 118,137, with a population density of 159.9 persons per square km.
Location and boundaries
The City of Ballarat is Victoria’s largest inland centre, located in south-western Victoria, about 110 kilometres west of the Melbourne CBD. The City of Ballarat is bounded by Hepburn Shire in the north, Moorabool Shire in the east, Golden Plains Shire in the south, and Pyrenees Shire in the west.
Traditional Owners
The original inhabitants of the City of Ballarat were the Wadawurrung and Dja Dja Wurrung Aboriginal people.
Name origin
The City of Ballarat is thought to be named from two Aboriginal words, “balla” meaning elbow or reclining on the elbow, and “arat” meaning place, signifying a camping or resting place.
Important
|
Population118,137 2023 ABS ERP |
Land area738.7 square km |
Population density159.9 persons per square km |
Settlement history
European settlement dates from the 1830s when sheep grazing and farming were established, followed soon after by a settlement at Buninyong. Gold was first discovered in the area in 1851, prompting the establishment of townships at Mount Clear, Sebastopol and Warrenheip. The township of Ballarat emerged as a service centre to the diggings, with land sales dating from 1852. Due largely to the gold rush, the population exploded, peaking at about 64,000 in 1868. During the 1870s other industries were established including woollen mills, flour mills, tanneries, boot-making enterprises, meat-preservation works, brick-making and breweries. When a recession hit the mining industry in 1870, the population declined significantly. However, the manufacturing industry and agricultural sector kept the economy afloat. The railway lines to Maryborough and Ararat were opened in 1875, enabling Ballarat to become a significant retail centre. In the late 1800s there were also timber industries, cordial factories and some vines and winemaking. Throughout the twentieth century Ballarat prospered as a major administrative, manufacturing and commercial service centre. The population of Ballarat increased significantly again in the post-war years. Most of this growth was in the west and north, in suburbs such as Ballarat North and Wendouree. The City had a relatively stable population for much of the 1980s and early 1990s, but has grown strongly since the mid 1990s, due largely to substantial employment growth in service industries and expansion of core manufacturing (food processing) and agricultural industries. This population growth was most heavily concentrated in the inner north suburbs of Alfredton, Invermay Park and Lake Gardens, and areas south of the City Centre such as Delacombe. More recently, growth has also been in Miners Rest and Sebastopol.
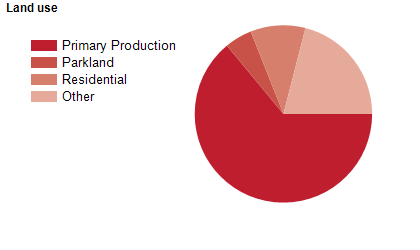
Land use
The City of Ballarat is predominantly a residential area, but also has substantial industrial, commercial and rural areas. It contains a number of lakes, reserves and parks. Industrial areas are located mainly in the inner north areas of Alfredton, Delacombe, Mitchell Park and Wendouree. The rural areas are located mainly in the far west and north, although many of these have a large element of rural-residential and rural living. Tourism is an important industry. The City of Ballarat encompasses a total land area of 739 square kilometres.
Transport
The City of Ballarat is served by the Western Freeway, the Midland Highway, the Glenelg Highway, the Sunraysia Highway, Ballarat Airport and the Ararat-Ballarat-Melbourne railway line.
Major features
- Major features of the City of Ballarat include Sovereign Hill,
- Ballarat Wildlife Park,
- Ballarat Bird World,
- Ballarat Aviation Museum,
- Ballarat Tramway Museum,
- Eureka Centre,
- Ballarat City Centre,
- Federation University (Camp Street,
- Mt Helen and SMB Campuses),
- Australian Catholic University (Ballarat Campus),
- Ballarat Base Hospital,
- St John of God Ballarat Hospital,
- Ballarat Botanical Gardens,
- Ballarat Aquatic & Lifestyle Centre,
- Ballarat Showgrounds,
- Mount Buninyong,
- Lake Wendouree,
- Lake Burrumbeet,
- Lake Learmonth,
- The Avenue of Honour and the Arch of Victory.
Included areas
- The City of Ballarat includes the suburbs and localities of Addington,
- Alfredton,
- Ascot,
- Bakery Hill,
- Bald Hills (part),
- Ballarat Central,
- Ballarat East,
- Ballarat North,
- Black Hill,
- Blowhard,
- Bo Peep (part),
- Bonshaw,
- Brown Hill,
- Buninyong (part),
- Bunkers Hill,
- Burrumbeet (part),
- Canadian,
- Cardigan,
- Cardigan Village,
- Chapel Flat,
- Coghills Creek,
- Creswick (part),
- Delacombe,
- Durham Lead (part),
- Ercildoune (part),
- Eureka,
- Glen Park (part),
- Glendaurel,
- Glendonald,
- Golden Point,
- Gong Gong,
- Invermay (part),
- Invermay Park,
- Lake Gardens,
- Lake Wendouree,
- Learmonth,
- Lucas,
- Magpie,
- Miners Rest,
- Mitchell Park,
- Mount Bolton,
- Mount Clear,
- Mount Helen,
- Mount Pleasant,
- Mount Rowan,
- Nerrina,
- Newington,
- Redan,
- Scotchmans Lead,
- Scotsburn (part),
- Sebastopol,
- Smythes Creek (part),
- Soldiers Hill,
- Sulky (part),
- Tourello,
- Warrenheip (part),
- Wattle Flat (part),
- Waubra (part),
- Weatherboard,
- Wendouree,
- Windermere and Winter Valley.